Product Review
-
 04/26/2022
04/26/2022How Safe Is Indoor Plumbing?
-

-
 01/13/2022
01/13/2022Does Queenslandmax work or is it a scam?
-
 01/11/2022
01/11/2022Chicwish Review: Merry Christmas to me!
-
 05/01/2022
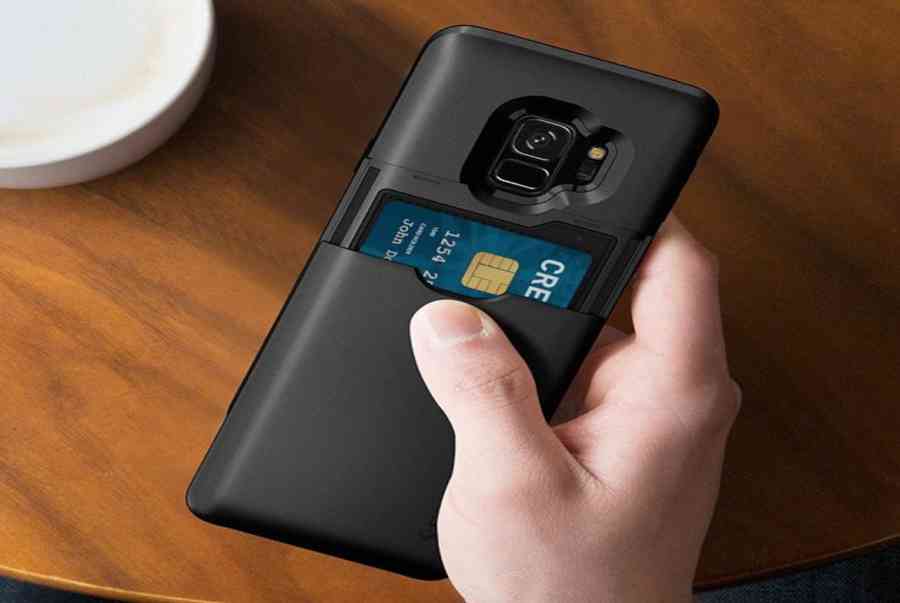
05/01/2022Samsung Galaxy S9 Cardholder Cases
-

-

-

-

-
 05/01/2022
05/01/2022Samsung A10 Cases
02/10/2024
Top 9 Most Profitable Blog Niches for 2024: Your Launchpad to Success
Choosing the right blogging niche is critical for building a thriving online presence. While “profitability” can be subjective, some niches…
02/01/2024
Celestial Harmony: Star Earrings Intertwined in Chic Chains
In the realm of fashion, accessories are the celestial stars that illuminate our attire. Among them, star earrings hold a…
01/18/2024
Mastering the Seas with 8721 g-G Mega Gloss 1-Part Marine Topside Polyurethane Enamel
Tips and Advice for Using 8721 g-G Mega Gloss 1-Part Marine Topside Polyurethane Enamel Marine enthusiasts, both seasoned professionals and…
01/18/2024
How to Grow Your Social Media Presence Organically in 2024
In today’s digital age, possessing a robust social media presence is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity. Whether you’re…
01/11/2024
44.904.376 Luiz Augusto Campos Engenharia Senges A Name Synonymous with Excellence and Trust
For years, the name Luiz Augusto Campos has been synonymous with engineering excellence and trust in the industry. With over…
01/07/2024
Introduction to ATK Hairy Models
ATK Hairy Models, also known as Amateur Teen Kingdom Hairy Models, have been a staple in the adult industry since…
12/18/2023
Dental Implants in New York – Improving Your Dental Health
Dental implants are the replacement of tooth roots. Implants provide a strong foundation for fixed or removable bridges or dentures.…
11/12/2023
Erek Erek Terlengkap: Unveiling the Secrets of Indonesian Dream Interpretation
Welcome to the fascinating world of “Erek Erek Terlengkap,” a rich tapestry of dreams and symbols deeply rooted in Indonesian…
07/28/2022
Biggest Social Media Platforms as Per User Base
The web is the sacred lifeline of industrial development as every one of the cutting-edge wonders that the world has…
07/15/2022
AniMixPlay Review – Is AniMixPlay Safe?
AniMixPlay is a website where you can watch anime for free. But is it safe? Is it licensed for anything?…
07/07/2022
The Benefits of Green Buildings
The term green building can be used to describe both the structure of a building and the processes that go…
06/23/2022
Pacman 30th Anniversary: New Google Doodle
A modified version of the Google doodle honoring Pacman 30th anniversary has been created. This wistful throwback game is an…
Home and Decor
01/04/2022
Tree Lopping Service
The logging service is provided and operated by Complete tree experts Tree services Sydney. It consists of a team of…
Business
01/26/2022
How to Create a Sprint Backlog
A sprint backlog consists of all the tasks to be performed. The Sprint Backlog provides additional context for the Daily…
News
04/12/2022
Project-based learning in AP classrooms: Lessons from research
Lectures are not the only way to prepare students for Advanced Placement exams. A critical challenge facing the public education…
Home and Decor
01/10/2022
Are You Looking to Hire the Best Carpet Cleaning Company?
You probably have chic and aesthetically pleasing carpets on your floor. But in the end, what matters is how long…
Education
01/13/2022
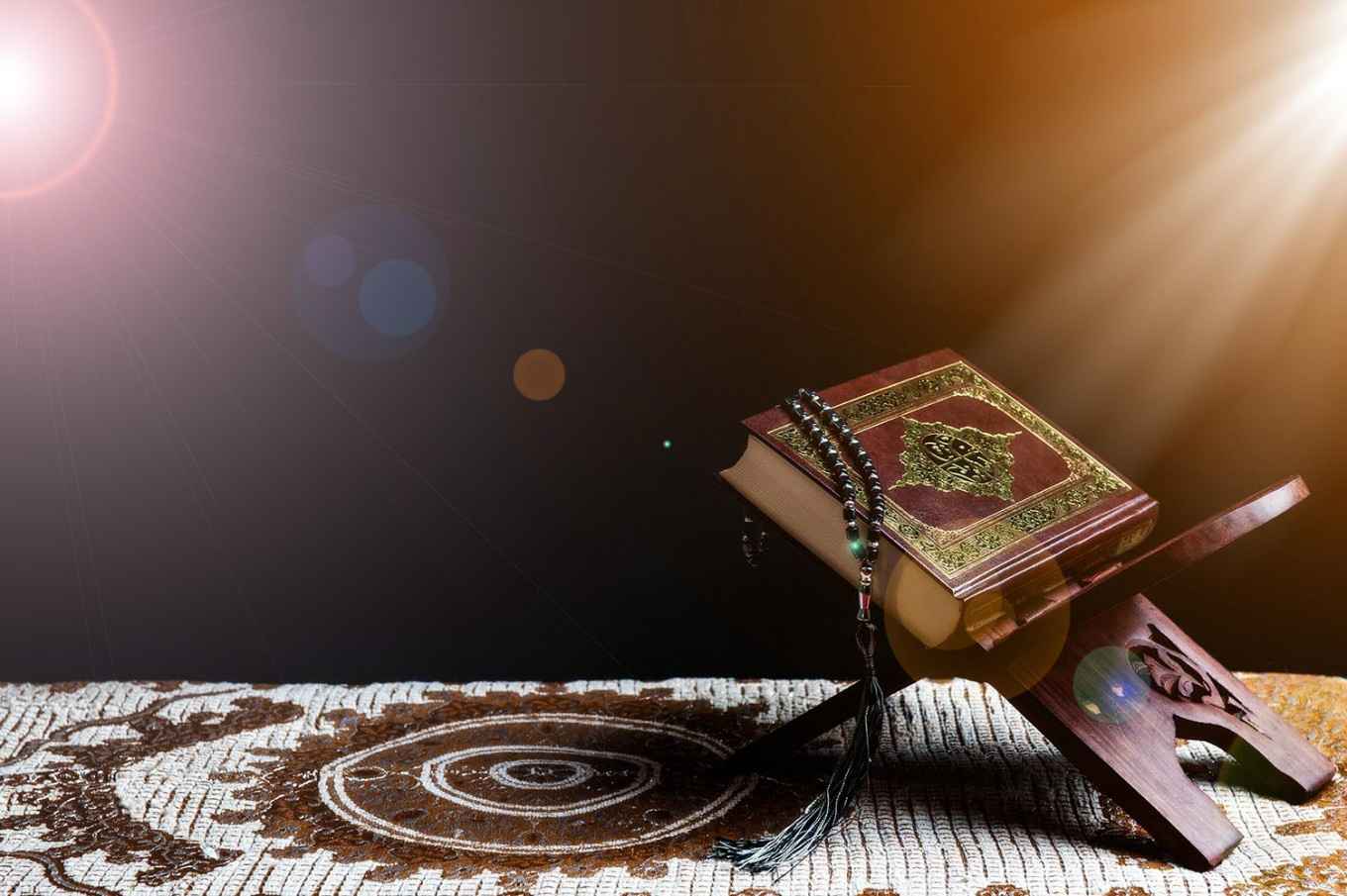
By 2022 online Quran study will be available in Canada
Whether you live in the US or Canada, one thing is certain: Muslims are everywhere. This has increased demand for…
Education
12/16/2021
Top 10 Useful Sources Of Incuweb
IncuWeb: Everything You Need To Know About It [Update] IncuWeb is an online wildfire incident information system where users can…
Uncategorized
01/13/2022
The Best Groomsmen Gifts (That They’ll Keep)!!!
You and your partner will put in a lot of effort to prepare for your wedding day, but there will…
Uncategorized
12/10/2021
Top 10 Useful Sources Of Anime Glass Painting
130 Anime glass painting ideas in 2021 – Pinterest Explore Kearstyn Gladden’s board “anime glass painting” on Pinterest. See more…
Uncategorized
09/25/2021
Finding The Best Reviews of VT Headsets
Are you interested in reading VT headsets review? There are quite a few of them on the Internet such as…
Business
02/05/2022
3 Simple Steps To Creating Personalized Ecommerce Experiences
It’s no secret that e-commerce has taken over the web. There are hundreds of millions of online stores and each…
News
04/14/2022
TogelUp APK Download Latest Version (v1.1)
TogelUp APK is an android monetization application that provides one of the biggest on-line count platforms for people. It provides…
Health
01/03/2022
How much does get abortion pills in Dubai abortion cost in 2022
1: I’m too old to have a baby Hello, I would like to tell my story. I am 41 years…
Health
01/01/2022
Build Your Own Business with White Label CBD Tinctures in Ohio
The growth of alternative healthcare is on the rise in Ohio as well as across. The United States mainly because…
Business
02/03/2022
Doubts You Should Clarify About PRO Services In Dubai
On the off chance that you are a customer, you would most presumably have caught wind of the term PRO…
Cryptocurrency
01/06/2022
How are Bitcoin ATMs Different from Traditional ATMs?
Bitcoin ATMs are a common site in Illinois. These are machines that look similar to traditional ATMs from where you…
Health
12/29/2021
low-calorie foods for Weight loss
With respect to getting more fit and administering it, Weight loss our overall expertise obliging it might be to screen…
Fashion
01/11/2022
Chicwish Review: Merry Christmas to me!
You’ve opened all the gifts under the tree. Now, find what you really want online. Fortunately, Chicwish is only a…
Uncategorized
02/04/2022
The Purpose and Type of Research
A research is coherent activities that begin with thinking about the topic or question. Following the data and information collection…