Essential Cloud Security Tips for Safer Cloud Use
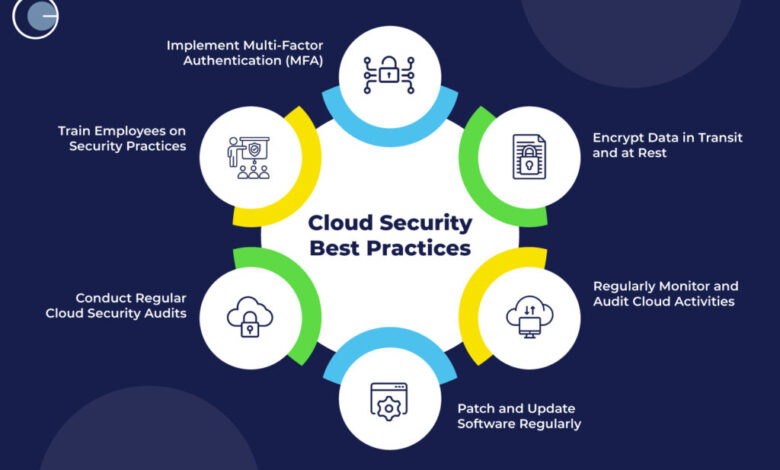
Table of Contents
Introduction
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses and individuals store, manage, and access data. From small startups to global enterprises, the cloud delivers speed, flexibility, and cost efficiency unmatched by traditional systems. But while cloud technology unlocks innovation, it also introduces risks. Cybercriminals are constantly seeking ways to exploit misconfigured services, weak access controls, or unencrypted data. The reality is that a single oversight can expose sensitive information, disrupt operations, or damage trust.
That’s why mastering cloud security is essential. Whether you’re an IT professional, a business owner, or simply a frequent cloud user, applying the right safeguards can help you avoid costly mistakes. This article outlines proven strategies to secure your cloud environment—covering everything from encryption and access management to monitoring, automation, and zero-trust design. By the end, you’ll have a clear, actionable roadmap for keeping your cloud environment secure and your data safe.
Key Cloud Security Tips
Understand the Shared Responsibility Model
Cloud providers secure the infrastructure—servers, networks, and physical facilities—but the user is responsible for securing data, applications, and configurations. Knowing where your responsibility begins helps prevent blind spots.
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Everywhere
Passwords alone are not enough. MFA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring additional proof, such as a text code, authenticator app, or hardware token. This simple step dramatically reduces unauthorized access.
Apply the Principle of Least Privilege
Every account, user, or service should have the minimum level of access needed to perform its job. Restricting privileges reduces the risk of insider threats and limits the damage of stolen credentials.
Monitor for Misconfigurations
Many cloud breaches result from simple errors—like leaving storage buckets public or mismanaging firewall rules. Continuous monitoring tools can detect and correct misconfigurations before attackers exploit them.
Encrypt Data in Transit and at Rest
Encryption makes data unreadable to unauthorized users. Protect files both while stored in the cloud (at rest) and while moving between systems (in transit).
Use Client-Side or Application-Level Encryption
For stronger control, encrypt data before it leaves your environment. Managing your own encryption keys ensures that only you decide who can access sensitive information.
Strengthen Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Implement strong identity verification and role-based access controls. Remove unused accounts promptly, rotate credentials, and regularly audit who has access to what.
Automate Security Audits and Hardening
Automated auditing tools can continuously check for vulnerabilities, policy violations, or outdated software. Immutable infrastructure (where systems are replaced instead of patched) further reduces risks.
Segment and Isolate Networks
Use micro-segmentation to divide your cloud environment into smaller, secure zones. If attackers breach one area, segmentation prevents them from moving freely across your network.
Monitor Continuously with Logging and Threat Detection
Set up logging, anomaly detection, and automated alerts. Combining monitoring with threat intelligence helps detect suspicious activity before it escalates.
Conduct Regular Penetration Testing
Simulating attacks on your cloud environment reveals vulnerabilities before real attackers do. Pen testing validates defenses and strengthens your incident response plan.
Maintain Reliable Backups
A strong backup strategy is your safety net. Automate backups, test them regularly, and store copies in separate locations to ensure quick recovery from ransomware or outages.
Adopt Zero-Trust Security
Zero-trust assumes no user, device, or application is automatically trustworthy. Every access request is verified, reducing reliance on network perimeters and enhancing overall resilience.
Consolidate Security Tools and Enforce Consistent Policies
Too many uncoordinated tools create blind spots. Centralize your security stack, enforce consistent policies, and integrate reporting across platforms for better visibility.
Follow Global Standards and Frameworks
Align with recognized standards such as ISO/IEC 27017 (cloud security controls) or ISO/IEC 27018 (protection of personal data). These frameworks provide assurance to customers and regulators alike.
Stay Vigilant Against Emerging Threats
Cyber threats evolve constantly. Keep up with industry advisories, patch vulnerabilities quickly, and update your cloud security policies regularly to stay one step ahead.
Read More: What Is a Gimkit Code and How to Use It
Conclusion
Cloud computing delivers unmatched convenience and scalability—but without strong security, it can also expose businesses and individuals to serious risks. Protecting your cloud environment means more than setting up passwords and hoping for the best. It requires a layered approach: clear responsibility, strong authentication, least-privilege access, encryption, and constant monitoring. Advanced practices like zero-trust architecture, automated audits, and network segmentation take defenses further.
Equally important is preparation—penetration testing, backup strategies, and adherence to standards ensure resilience when incidents occur. By following these best practices, you safeguard not just your systems but also your reputation, compliance standing, and customer trust.
The key takeaway: cloud security is not a one-time task but a continuous discipline. With the right mindset and proactive measures, you can confidently embrace the cloud’s power while minimizing its risks.
FAQs
1. Why is the shared responsibility model important in cloud security?
It defines what the provider secures and what the customer must secure. Understanding this division prevents dangerous gaps in protection.
2. How does encryption improve cloud security?
Encryption transforms data into unreadable code, ensuring that even if attackers intercept it, they cannot access its contents without the decryption key.
3. What is the principle of least privilege?
It’s the practice of granting users and applications only the minimum access rights they need. This limits damage if an account is compromised.
4. Why should I monitor for cloud misconfigurations?
Misconfigurations are a leading cause of breaches. Continuous monitoring detects issues early and prevents accidental data exposure.
5. What does zero-trust mean in cloud security?
Zero-trust assumes no user or system is trusted by default. Every access request must be authenticated, authorized, and verified—reducing insider and external risks.



