Product Review
-
 01/11/2022
01/11/2022Chicwish Review: Merry Christmas to me!
-

-
 05/01/2022
05/01/2022Samsung A10 Cases
-

-

-
 01/13/2022
01/13/2022Does Queenslandmax work or is it a scam?
-

-
 05/01/2022
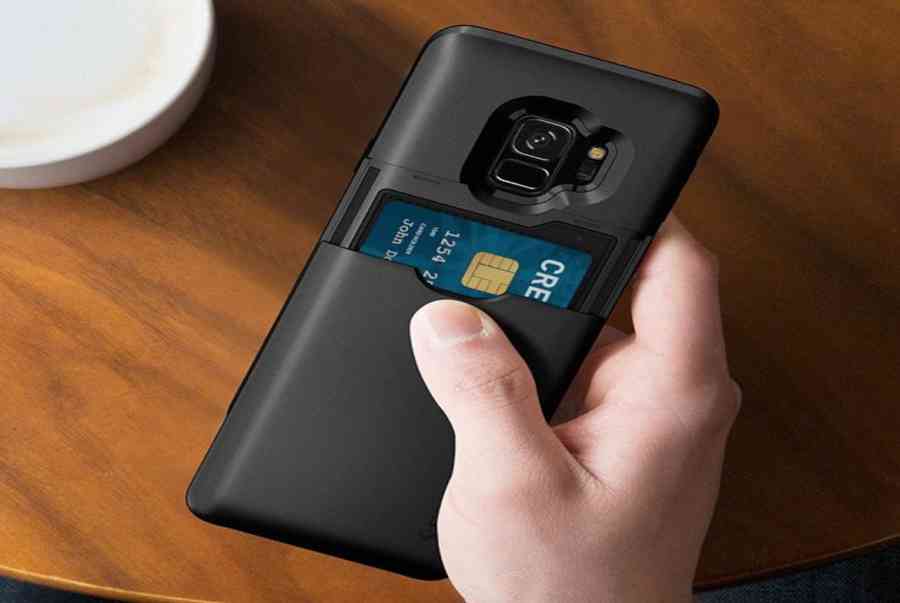
05/01/2022Samsung Galaxy S9 Cardholder Cases
-

-

02/10/2024
Top 9 Most Profitable Blog Niches for 2024: Your Launchpad to Success
Choosing the right blogging niche is critical for building a thriving online presence. While “profitability” can be subjective, some niches…
02/01/2024
Celestial Harmony: Star Earrings Intertwined in Chic Chains
In the realm of fashion, accessories are the celestial stars that illuminate our attire. Among them, star earrings hold a…
01/18/2024
Mastering the Seas with 8721 g-G Mega Gloss 1-Part Marine Topside Polyurethane Enamel
Tips and Advice for Using 8721 g-G Mega Gloss 1-Part Marine Topside Polyurethane Enamel Marine enthusiasts, both seasoned professionals and…
01/18/2024
How to Grow Your Social Media Presence Organically in 2024
In today’s digital age, possessing a robust social media presence is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity. Whether you’re…
01/11/2024
44.904.376 Luiz Augusto Campos Engenharia Senges A Name Synonymous with Excellence and Trust
For years, the name Luiz Augusto Campos has been synonymous with engineering excellence and trust in the industry. With over…
01/07/2024
Introduction to ATK Hairy Models
ATK Hairy Models, also known as Amateur Teen Kingdom Hairy Models, have been a staple in the adult industry since…
12/18/2023
Dental Implants in New York – Improving Your Dental Health
Dental implants are the replacement of tooth roots. Implants provide a strong foundation for fixed or removable bridges or dentures.…
11/12/2023
Erek Erek Terlengkap: Unveiling the Secrets of Indonesian Dream Interpretation
Welcome to the fascinating world of “Erek Erek Terlengkap,” a rich tapestry of dreams and symbols deeply rooted in Indonesian…
07/28/2022
Biggest Social Media Platforms as Per User Base
The web is the sacred lifeline of industrial development as every one of the cutting-edge wonders that the world has…
07/15/2022
AniMixPlay Review – Is AniMixPlay Safe?
AniMixPlay is a website where you can watch anime for free. But is it safe? Is it licensed for anything?…
07/07/2022
The Benefits of Green Buildings
The term green building can be used to describe both the structure of a building and the processes that go…
06/23/2022
Pacman 30th Anniversary: New Google Doodle
A modified version of the Google doodle honoring Pacman 30th anniversary has been created. This wistful throwback game is an…
Uncategorized
01/13/2022
The Best Groomsmen Gifts (That They’ll Keep)!!!
You and your partner will put in a lot of effort to prepare for your wedding day, but there will…
Cryptocurrency
12/28/2021
Bitcoin Scam: How To Avoid Them?
As you become more involved with the new digital monetary systems known as cryptocurrencies, you quickly realise that there is…
Health
12/18/2023
Dental Implants in New York – Improving Your Dental Health
Dental implants are the replacement of tooth roots. Implants provide a strong foundation for fixed or removable bridges or dentures.…
Health
01/12/2022
10 Amazing Health Benefits of Flaxseed, According to a Nutritionist
It’s no big surprise that the little, palatable seeds of the flax plant (which is perhaps the most seasoned yield…
Home and Decor
10/01/2021
Popfindr- Advantage and Disadvantage
Have you ever heard about Popfindr? This article will tell you about this interesting online store. What Is Popfindr? Popfindr…
Entertainment
07/15/2022
AniMixPlay Review – Is AniMixPlay Safe?
AniMixPlay is a website where you can watch anime for free. But is it safe? Is it licensed for anything?…
Digital Marketing
01/04/2022
Types of Search Engine Marketing
INTRODUCTION There are three types of search engine marketing: PPC, local SEO, and organic marketing. All of these types differ…
Business
02/05/2022
Why You Should Hire a SEO Specialist to Help Your Blog Grow.
Blogging has changed in the last decade and many bloggers are now looking for ways to improve their blog’s visibility.…
Uncategorized
12/10/2021
Top 10 Useful Sources Of Master Splinter
Master Splinter | TMNT Wiki | Fandom Master Splinter is the teacher and adoptive father of the Ninja Turtles. He…
Health
02/03/2022
Bimatoprost Containing Eyelash Growth Serum
Careprost is a very efficient medication that boosts an increase in the size of your eyelashes creating them darker and…
Uncategorized
09/03/2021
How to Buy Facebook Like in Australia – How to Get Started
Buying Facebook likes in Australia is a lot like shopping for any other products online. You want to buy what…
Uncategorized
01/04/2022
What is atypical pneumonia?
Winters for specialists Pulmonologist in Lahore like means influx of patients with respiratory illnesses like pneumonia. When the latter is…
Health
01/03/2022
How much does get abortion pills in Dubai abortion cost in 2022
1: I’m too old to have a baby Hello, I would like to tell my story. I am 41 years…
Health
01/03/2022
Amazing Health Benefits of Litchi
The Amazing Fruit Litchi Litchi can be a local USA organic product; be that as it may, its development has…
Fashion
04/12/2022
Radio personality Rachel Steele adopts more mature fashion sensibility: Fashion Flash
Reading: Radio personality Rachel Steele adopts more mature fashion sensibility: Fashion Flash Rachel Steele, 35, Mentor Music director and afternoon-drive…
Health
04/16/2022
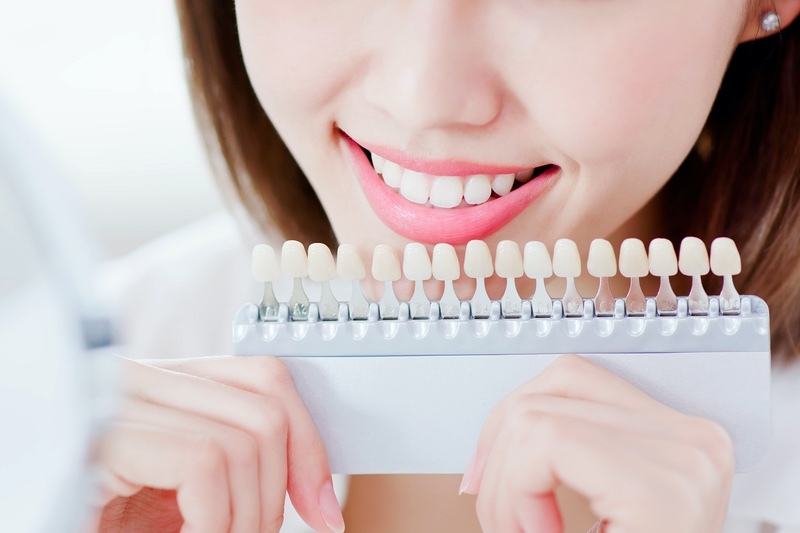
Ways Cosmetic Dentistry Can Improve Your Oral Health
In recent times, cosmetic dentistry has become more popular than ever. While many people may be wary of getting anything…
Uncategorized
02/01/2022
iPhone Activation Lock Removal Official Application For All iOS Users
You can use iPhone Activation Lock Removal to unlock your iCloud account. You might lose your login credentials and your iDevice…
Home and Decor
09/25/2021
Choosing a Diamond Home Improvement Contractor
About Diamond Home Improvement What is Diamond Home Improvement? The question may seem like the sort of random trivia you…